OSM Open-Street-Map overlay collections COOL:
- https://www.dublinhistoricmaps.ie/
- e.g. Dublin Metropolitan Police 1838, 1840, 1901 https://www.dublinhistoricmaps.ie/boundaries/dmp/index.html
e.g. see 1776 Plan of Dublin https://www.dublinhistoricmaps.ie/maps/1600-1799/index.html
Another list of maps: https://libguides.ucd.ie/findingmaps/mapshistDublin
Oldest bridge in Dublin across the Liffey:
| Father Mathew Bridge | Whitworth Bridge, Dublin Bridge, Old Bridge | Road bridge | Church Street to Bridge Street Lower | 1818 (Previous structures: 1014, 1428) |
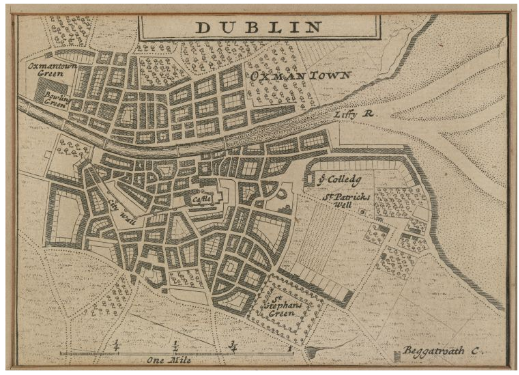
c1000 Ford of Áth Cliath, Vikings build simple wooden bridge
c1214 Stone Bridge granted by King John built near site of older Viking bridge
1385 King John's Bridge is swept away by floods.
1428 New bridge built, called Friar's Br./the Br./Old Br./Dublin Br.
1610/1612 Dubline Speed
https://www.lbrowncollection.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/Dublin-Speed-1612.jpgA scale of Pases 50 100 150 200
North side 1. S.Mihans church and to east 2. S.maryes Abbey swamp/water by part of side by river
One bridge 5 - The Bridge, between 4. Ormunton - 29. Ormonds Gate, and 3. The innesJust to west of bridge 2 streams join and enter liffey river.
The east of bridge on South side of river:
9. Marchants Key 25. Wine tavern Stret 8. Wood quay 7. Fians Castle 6. Newmans Tour
To the east of map 12. The Colledge, 10. The Hospitall, 13. Bridewell 14. Damas Stret, 16. St Andrews church, 15. Damas GateHarbour? Water comes in under Dame's St. and moat by wall to 39. Pole Gate and 45. S. Nicholas Gate 56. to the West St James's Gate on the Slí Mór and 57. St Catherine's Church
https://drb.ie/a-pase-around-old-dublin/ John Speed's map of Dublin - part of the Theatre of the Empire of Great Britain, atlas published in 1612 |
| Dubline - map with A scale of pases and lists of locations - Speed - 1612 |
More clear map by Speed 1610:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxmantown#/media/File:Views_of_the_most_remarkable_public_buildings,_monuments_and_other_edifices_in_the_city_of_Dublin_(1780)_(14772904475).jpg
https://www.lbrowncollection.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/Dublin-Ireland-4-towns-Gerard-Mercator-1633-2.jpg
 |
| The Dublin part of the 4 cities map |
1650-1680 TODO ...
1665 Ferry services across liffey granted charter by King Charles II
1680-1684 Royal Hospital Kilmainham built to accomodate former soldiers
https://imma.ie/heritage-trail/royal-hospital/
5 bridges in city centre by 1684 (4 added in 1670 1676 1683 1684) boom time
upstream:
| Anna Livia Bridge | Chapelizod Bridge | Road bridge | Lucan Road to Chapelizod Road | 1753 (Previous structure: 1660s) |
city centre:
| Rory O'More Bridge | Victoria & Albert Bridge, Queen Victoria Bridge, Bloody? | Road bridge | Watling Street to Ellis Street | 1859 (Previous structures: 1670, 1704) |
| Mellows Bridge | Mellowes Bridge, Arran Br., Queen's Bridge, Queen Maeve Bridge | Road bridge | Queen Street to Bridgefoot Street | 1768 (Previous structure: 1683)
OLDEST SURVIVING |
| Father Mathew Bridge | Whitworth Bridge, Dublin Bridge, Old Bridge | Road bridge | Church Street to Bridge Street Lower | 1818 (Previous structures: 1014, 1428)
OLDEST |
| Grattan Bridge | Essex Bridge | Road bridge | Capel Street to Parliament Street | 1874 (Previous structures: 1676, 1755) |
Essex is the lowest/east-most bridge (in 1756)
connects Capel St to Parliment St (to Dame St. / College Green)
Charles Brooking 1677-1738 active in Plymouth and Ireland maybe created this map, his son painter:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Charles_BrookingBridges: Essex, Ormond, Old, Arran, Bloody
Arran bridge from Queen St, Bloody Bridge to Watling St.
1753 Chapelizod Bridge is built
1751-1756 Comissioners of Inland Navigations Established - CANALs start
https://archive.waterwaysireland.org/history-of-the-waterways/9/the-history-of-the-grand-canal
1755 survey made to find route for Royal Canal
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Royal_Canal
1756 work starts on Grand Canal Scheme
1773 foundation stone of 1st lock laid
1753-5 Essex Bridge RE-built by George Semple
1751 Semple boasts he can repair Essex bridge. And is comissioned to reconstruct it completely.
He read and consulted and .. read more in "Forest de Bélidor's Architecture hydraulique, ou l'art de conduire (4 vols, Paris, 1737–53), which detailed the use and advantages of coffer dams. These enclosures were pumped dry of water, facilitating the building of solid foundations. The method, then in its infancy, compared to caissons – large enclosed sections of masonry sunk to the river bed – which Labelye used at Westminster. Semple adopted the ‘daring’ (Casey, 31) coffer-dam technique, the first time this method was used in Ireland."
"The bridge, completed (1755) at a cost of £20,661, after two years and eighty days of uninterrupted construction,"
"The foundations remain in use, being retained when the superstructure of Semple's bridge was replaced (1873–4) by Grattan Bridge."
1757 Smock Windmill Tower built off Watling St / Thomas St to power Roe's whiskey distillery
http://builtdublin.com/smock-tower-watling-street-dublin-8/
https://www.buildingsofireland.ie/buildings-search/building/50080329/saint-patricks-tower-thomas-street-watling-street-dublin-8-dublin
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/St_Patricks_Tower
https://peartreecrossing.ie/history/
1757 - St Patrick's Hospital aka "Swift's hospital" is completed
Built by George Semple.
"a hospital for the mentally ill in Dublin, fulfilling the bequest of
Jonathan Swift"
"Semple acquired (1754) land on Queen St., Oxmantown, Dublin, building a number of houses there, and residing there for the remainder of his life. He built houses on Capel St.", and other places in Dublin and around Ireland.
1762 Merrion Square is laid out.
1764 Bellin
https://archive.org/details/dr_plan-de-la-ville-de-dublin-6903367 <- PRETTY and GOOD
image
plan de la Ville de Dublin.
- by
- Bellin, Jacques Nicolas, 1703-1772; J. Arrivet
- "Bellin was an important maker of charts for the French Depot de la Marine. "
- "The Petit Atlas Maritime is probably the best compilation of plans of maritime towns and harbors of its time. Colour version found here:
- https://www.lbrowncollection.com/maps-of-ireland-part-9-dublin-1717-1890-dg005-i-dg200/
- There are (still?) 5 bridges across Liffey in 1764.
Bridges: Essex, Ormond, Old, Arran, Bloody
| Rialto Bridge | Harcourt Bridge (official name) | Over Luas Red Line South Circular Road - R811 | This was on the former main line of the Grand Canal. During the construction of the canal a temporary wooden bridge was built in 1766.[28] in 1795 an elegant stone bridge was constructed,[29] which lasted until 1939 when a new wider concrete bridge was built. In 1974 the canal section was filled in. When the Luas Red Line was opened in 2004 the bridge was altered with the parapet raised above eye level. Original name of bridge comes from Simon Harcourt, 1st Earl Harcourt, Lord Lieutenant 1772–76. The name Rialto comes from a local area and is not related to the Italian Rialto Bridge. |
Bridges across the new Grand Canal open in 1791
- (1791 I think? Work on canal started in 1956)
Across Grand Canal Dock:
| MacMahon Bridge | Draw Bridge, Brunswick Bascule,[5] Victoria Bridge (1857 and 1900 bridges) | Ringsend Road, Pearse Street - R802 | Named after General Seán Mac Mahon. Rebuilt in 2007. Previous bridges in 1791, 1857, 1900 and 1960[6] (or possibly 1962[7]). |
More canal bridges built in 1791 .. all along the Grand Canal ?- :- Maquay Bridge, Grand Canal St.
- :- Mount St. bridge aka McKenny's Bridge, Coyningham Bridge
- :- Huband Bridge
- :- Macartney Bridge sks Baggot St. Bridge
- :- Eustace Bridge aka Leeson St. Bridge :- Charlemont 6th lock and Luas bridge 2004
- :- La Touche Bridge aka Portobello Bridge
- :- Robert Emmet Bridge aka Clanbrassil Bridge, Harold's Cross Bridge
- :- Parnell Bridge aka Sally's Bridge, Clogher Rd.
- :- Camac Bridge aka Dolphin's Barn Bridge
- :- Herberton Bridge aka Haberton Bridge, others ? Griffith Bridge ? ...
 |
| Huband Bridge in 1936, painting by Harry Kernoff (this artist has a few other nice works of Dublin |
- 1766 a wooden bridge Harcourt Bridge aka Rialto Bridge 1975 stone
- Near Rialto, Grand Canal 1st lock there are now 2 bridges.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rialto_Bridge - across the Grand Canal in Venice
https://www.dublincity.ie/library/blog/rialto-bridge
- http://eiretrains.com/Photo_Gallery/Railway%20Stations%20C/Charlemont/IrishRailwayStations.html
| Ballyfermot Bridge | | Old Killeen Road | Built around 1775.[31] |
- 1768 The Queen’s Bridge is built.
1776
| Aylmer's Bridge | | Lyons Road - L5064 | Built in 1782 or 1784, depending on sources. Lies on the border between County Kildare and County Dublin. |
1790 Royal Canal under construction
Work on the Royal Canal commenced in May 1790 at Cross Guns Bridge, Phibsborough in a westerly direction towards Ashtown. Smaller canal 500m to Broadstone
- Blacquiere humped back Bridge constructed to carry new North Circular Road over canal.
- Fosters Aqueduct to take canal over Constitution Hill road
- large harbour dug as terminus
1802 Broadstone section of canal started work - service to Newcastle near Enfield
3 pictures:
 |
| Foster Aqueduct (view of the city of Dublin) |
1791 Grand canal also under construction
John Killaly engineer with the Grand Canal Company and subsequently appointed Chief Engineer to the Director General of Inland Navigation.
1792 Sarah Bridge, now Island Bridge, is built downstream of the old, ruinous structure.
1796 Brunswick wooden bascule bridge over grand canal
Brunswick St. is now Pearse St.
Replaced after a few years by metal version and rebuilt by 1857 as the Victoria Bridge.
https://www.lbrowncollection.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/DG031-Dublin-William-Faden-1797.jpgA plan of the city of Dublin as surveyed for the use of the Division justices to which have been added plans of the CANAL HARBOUR and its JUNCTION with the Grand Canal, the Royal Canal and every projection and Iteration to the Present time 1797.
1804 Corbet map
Bridges: 5 - Carlisle(new(ish)), Essex, .. (Ormond bridge is gone), Old Br., Queen's (was Arran), cannot read (was Bloody)
 |
| New Plan of the City of Dublin - by W. Corbet, 57 Gt. Britain St. opposite Granby Row - 1804 |
1807 picture of Liffey facing the Four Courts by Thomas Roberts
I think the ruined bridge is the Ormonde bridge. Old Dublin bridge in background.
1810 a reservoir, the Blessington Basin, is dug from the Royal Canal/Broadstone spur to supply water to the locality.Military road goes from Watling St West to Royal Hospital Kilmainham and continues outside hospital wall beside the Liffey to Islandbridge. |
| Barrack/Bloody Bridge and Watling St. Gatehouse |
1811 Gregory map https://www.lbrowncollection.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/DG039-i-Dublin-W-Gregory-1811.jpg Bradogue River marked. Bridges on Liffey: H?illegible, Queens, Old Bridge, .. (Ormonde/Richmond bridge is gone), Essex, Carlisle
1816 Richmond Bridge built to replace the old Ormonde bridge which had been destroyedhttp://www.bridgesofdublin.ie/gallery/view/richmond-bridge-1910"He modernised Essex (Grattan) Bridge (1808–9) and Arran (Mellowes) Bridge (1816–18) with cast metal features. His new bridges included Richmond (O'Donovan Rossa) Bridge (opened 1816, replacing the flood-damaged Ormonde Bridge) and Whitworth (Father Mathew) Bridge, opened 1818"
1816 Wellington Bridge, now familiar as Dublin’s iconic Ha’penny Bridge, opens. Ha'penny toll charged.
Wellington not popular as name so it is called locally the Metal Bridge
Beside ferry at Fownes St. Lower / Bagnio Slip.
1817 Royal canal reaches Shannon river and Broadstone Harbour is major connection to midlands.
 |
| Royal Canal Harbour, Broadstone, Dublin |
1817 Dublin city, Cadell and Davies
7 bridges: Carlisle, ?Iron(Ha-penny/Liffey/Metal/Wellington), Essex, Richmond(is back), Whitworth(old bridge is renamed), illegible(presume Queens), illegible(Bloody?)
nice colouring, rivers/streams are given blue colour
 |
| 1817 Dublin city, Cadell and Davies |
1818 Whitworth Bridge, now Father Mathew, replaces the Old Bridge of 1428.
"He modernised Essex (Grattan) Bridge (1808–9) and Arran (Mellowes) Bridge (1816–18) with cast metal features. His new bridges included Richmond (O'Donovan Rossa) Bridge (opened 1816, replacing the flood-damaged Ormonde Bridge) and Whitworth (Father Mathew) Bridge, opened 1818"
In 1800 George Helpin was made Inspector of Works for the Dublin Ballast Board.
The first Bull Bridge, a wooden bridge is built to facilitate construction of the stone Bull Wall.
Started in 1820, the wall was completed in 1825.
"Over the succeeding 48 years, the natural tidal effects created by the two sea walls deepened the entry to the Liffey from 1.8 m to 4.8 m. Much of the silt now scoured from the river course was deposited on the North Bull"
"Halpin built new quay walls on the Liffey from Carlisle Bridge (built by
James Gandon (qv)) to Custom House Quay and George's Quay. By 1820 he had also rebuilt and enhanced those extending from Carlisle Bridge up to the official westward limit of the port jurisdiction at Bloody Bridge (Rory O'More Bridge), by the junction of Usher's Island and Watling St."
The Ballast Board became responsible for lighthouses in 1810.
... "Dublin lights at Howth Baily (1814) and the reconstructed Poolbeg (1820),"
1819 Byrne map
- https://www.lbrowncollection.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/DG043-Dublin-Joseph-Byrne-1819-p.jpg
- Byrne's Map of the City and Environs of Dublin.
- red city boundary
- yellow parishes
- Sarah Bridge + 7 bridges: Carlisle, ?Iron, ?Essex, ?Richmond, ?Whitworth, Queens, not named (Bloody?)
1820 Bianconi Stage Coach company regular road transport
1828 King’s Bridge, now Sean Heuston, opens to the public.
1830
1830(I think) Dublin, from Blaquiere Bridge, Royal Canal
1834 Dublin's first railway from Westland Row to Salthill near Kingstown (now Dun Laoghaire) openshttps://www.thehistorypress.co.uk/articles/10-facts-about-the-first-irish-railway/
1834 - quay wall improvements - George Halpin
British consultant engineer William Cubitt recommended that the north and south quays of the lower Liffey be enlarged and strengthened to meet the increased volume of shipping. Restricted by cost, Halpin and his son undertook less expensive works, which in 1836 formed timber-piled wharves and embankments at the junction of the East and North Walls. The resulting North Wall Basin became generally known as Halpin's Pond (or Pool), subsequently named Alexandra Basin after Stoney's monumental extension of the Halpin project (1885).
Halpin added similar wharves (1840–42) at the North Wall, adjacent to the Royal Canal Dock.
1840 - Broadstone
 |
| Broadstone harbour, Royal Canal. Also North Dublin Union workhouse, Queen's Inns, Law Library, Fosdter Aqueduct over Constitution Hill, Royal Canal House and Terrace, Palmerstone Terrace, city and/or parish boundary lines junction. |
1845 Tallis map
https://www.lbrowncollection.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/Dublin-Tallis-1845.jpg <- GOODTallis map stretching from Richmond Barracks to the West ..Showing Kingsbridge railway station and GS&WR line heading out West.The Grand Canal looping South of the city across to Grand canal dock.Ringsend and the Dodder at the Eastern extent of map.The Dublin and Kingstown railway line heading from ?__ station on Westland Row out SE ..The Dublin and Drogheda rail line heading out to NE from Amiens St. station (opened in 1844, initially trains from temporary station on Royal canal)The MGWR line heading off NW from Broadstone station.
1845 a new railway company The Midland and Great Western Railway Company (MGWR) purchased the entire royal canal and its harbours. In 1848 they had carved a new train line (left) from Broadstone harbour running north along the western edge of Phibsboro running under the North Circular road. Once this line opened in 1848 carrying a train service from Broadstone to Mullingar the canal could not compete for passenger traffic.
1846 picture of City basin and Grand Canal Harbour
- 1846 Kingsbridge Railway Station is built on former hospital grounds, Watling St. Gatehouse causes congestion for increased traffic and it is moved to West entrance of Kilmainham Royal Hospital and renamed Richmond Tower
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Richmond_Tower_(Kilmainham)  |
| Kingsbridge(now Heuston) Railway Station building, Dublin |
1850 Neo-Egyptian train station opened at Broadstone
Broadstone name derives from the Norse Steyn (stone bridging) and Gaelic/Irish Bradán(salmon) óg(young) "Bradogue Steyn", due to the Bradogue River crossing the road to Finglas at this location. aka Bradoge, Bradok, Glascoynock, the Pole Water, St Michan's Streams, Le Rughdich
Leisute trips for middle classes grow. Possible to visit horse fairs, hunts etc and return on same day.
1852 canal passenger boats (on Royal and Grand canals) widthdrawn due to competition with railways
1856 Broadstone Railway Station (and Broadstone Harbour)
 |
The Broadstone Station, from tourist handbook by David Bryce
|
1861 Victoria and Albert Bridge, now Rory O’More, opens to the public.
1872 - New Dublin Quay wall build
 |
| 3. New Quay wall 1872-3, 2. old wall ?1800, 1. oldest quay wall 1714, river bed, low water, high water and ancient foreshore level with filling to existing quay level shown |
1875 New bridge by Bindon Stoney, later to be named Grattan Br., opens. It replaces the Essex Bridge of 1755. It keeps the foundations of the older bridge by George Semple.
1877 The Liffey Viaduct, a continuation of the railway line from Heuston Station across the Liffey, opens.
1877,78 Broadstone harbour (Royal canal line) partially filled in (access to railway prior to this was via pontoon bridge)
1879 Butt Bridge (1879 - 1929) Dublin City, ...
the first Liffey bridge in Dublin to be built with reinforced concrete, courtesy of Gray's Ferro- Concrete (Ireland) Ltd. Most Easterly bridge.
1880 O’Connell Bridge opens
1891 The Loopline rail Bridge opens.
1919 Ha'penny Bridge toll is abolished
1885 - Alexandra basin
The North Wall Basin known as Halpin's Pond (or Pool) is greatly extended by
Bindon Blood Stoney.
It is subsequently named Alexandra Basin.
1877-9 Beresford bridge / Butt Bridge
Stoney built a new iron swivel bridge in 1877–9, just west of the Custom House. Named Beresford Bridge, it was later renamed Butt Bridge after
Isaac Butt (qv), and replaced by a wider concrete bridge in 1932.
1888 Smock Tower and Roe Distellery c 1888
looking East along Thomas St I think
 |
| Smock Tower and Row whiskey distellery c 1888 |
1906 rail and tram
- https://www.lbrowncollection.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/Dublin-Bacon-Trams-1906.jpg
- NEW PLAN
- of
- Dublin
- and
- Suburbs
- Railways, thus: Tramways, thus:
1911 Midland and Great Western Train Company opens first bus service
1924 New Free State of Ireland consolidates railways into The Great Southerm Railway(GSR) company. Several train stations close including Broadstone which becomes a bus station.
1930s Blacquiere bridge in Phibsboro (Broadstone/Royal Canal line) is taken down. Canal filled in and transformed into public park, library, playground - Royal Canal Park.
1920s-30s-40s-50s-... Harry Kernoff (1900-1974) Irish artist paints Dublin landmarks, street scenes, pub characters
Dec 2021 - The Liffey Press republished Kevin O’Connor’s 2012 ‘Harry Kernoff, The Little Genius’, biography with pictures.
- National Library Collection list: https://www.nli.ie/sites/default/files/2022-12/harrykernoffpd2090tx.pdf
 |
| Harry Kernoff - Whiskey row Ringsend, Dublin |
1943 baile áta cliath : sketch development plan : metropolitan area.
- https://www.lbrowncollection.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/Dublin-Planning-Map-1943.jpg
- Circles. M50 and ring roads.
1951 Foster's Aqueduct in Broadstone is demolished
https://irishwaterwayshistory.com/abandoned-or-little-used-irish-waterways/waterways-in-dublin/
https://irishwaterwayshistory.com/abandoned-or-little-used-irish-waterways/waterways-in-dublin/the-broadstone-line-of-the-royal-canal/
Broadstone Harbour
King's Inns park would have been part of Broadstone harbour
EXPLORE: Linear park - from Broadstone Community Garden, Royal Canal Bank Playground, to Blessington St basin/Park and on beside Royal Canal Bank road continue under/over Blaquiere bridge and on past the back of Mountjoy Prison to the Royal Canal itself.
The Broadstone station was train station, then bus.
The Foster Aqueduct.
https://web.archive.org/web/20120328010605/http://irishhistorypodcast.ie/2011/02/17/broadstone-station-%E2%80%93-a-forgotten-history-of-dublin/
World history of canals:
https://archive.waterwaysireland.org/stories-and-exhibitions/story/21/a-potted-history-of-canals
http://www.bridgesofdublin.ie/
http://www.bridgesofdublin.ie/historical-dublin/city-maps
840c 1300 1610 ...
http://www.bridgesofdublin.ie/historical-dublin/timeline
Outside Dublin:
Dublin Bay:
Military Road:
- https://www.lbrowncollection.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/Dublin-Military-Road-Sally-Gap.jpg
- Sketch of that part of the New Military Road
- which extends from
- Mount Venus to Sally Gap
- and to
- Kilmalin
- NB The new Road is marked Red, the old Road's Brown.
 |
- Sketch of that part of the New Military Road
- which extends from
|